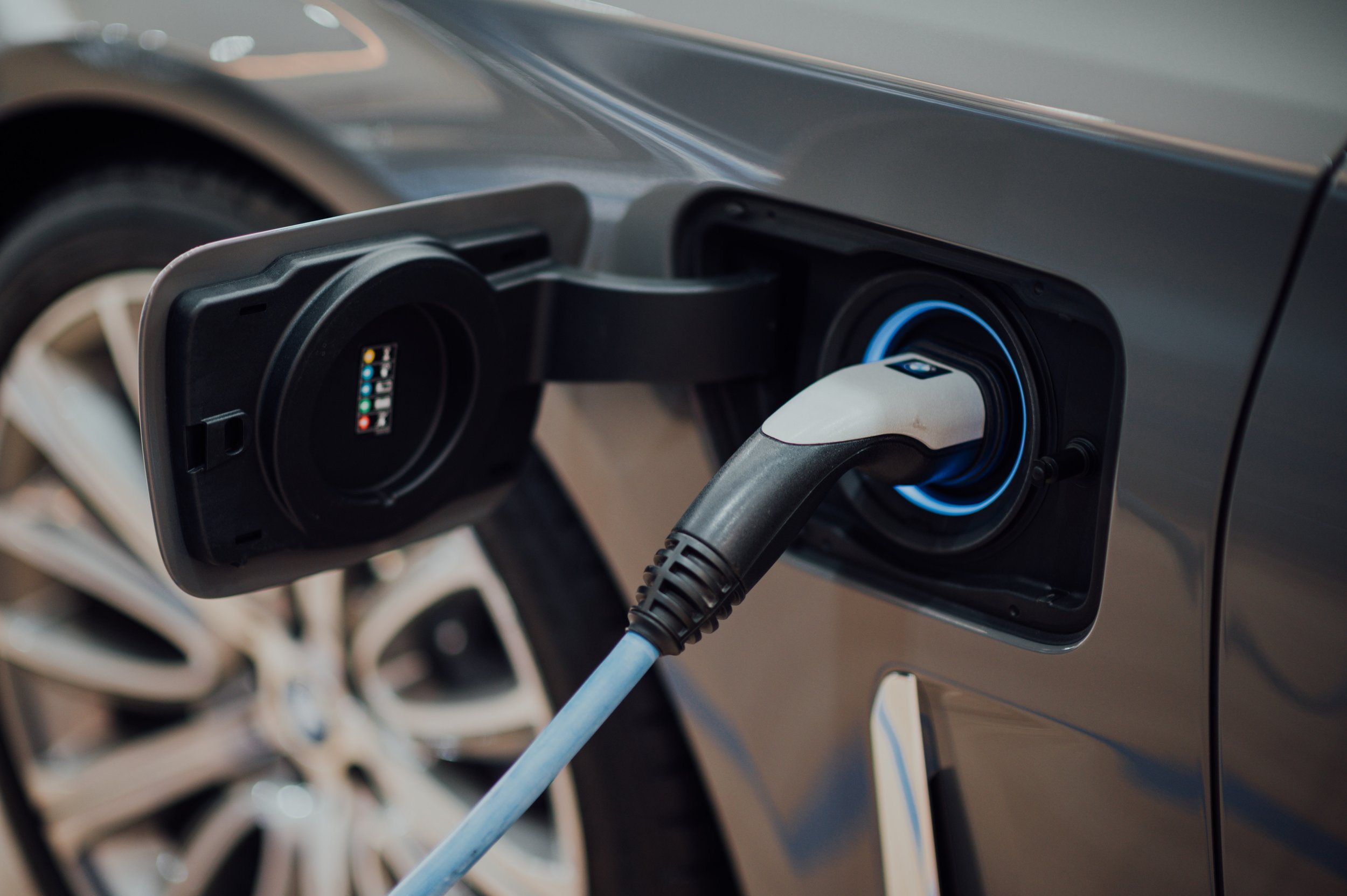
Building Electrification
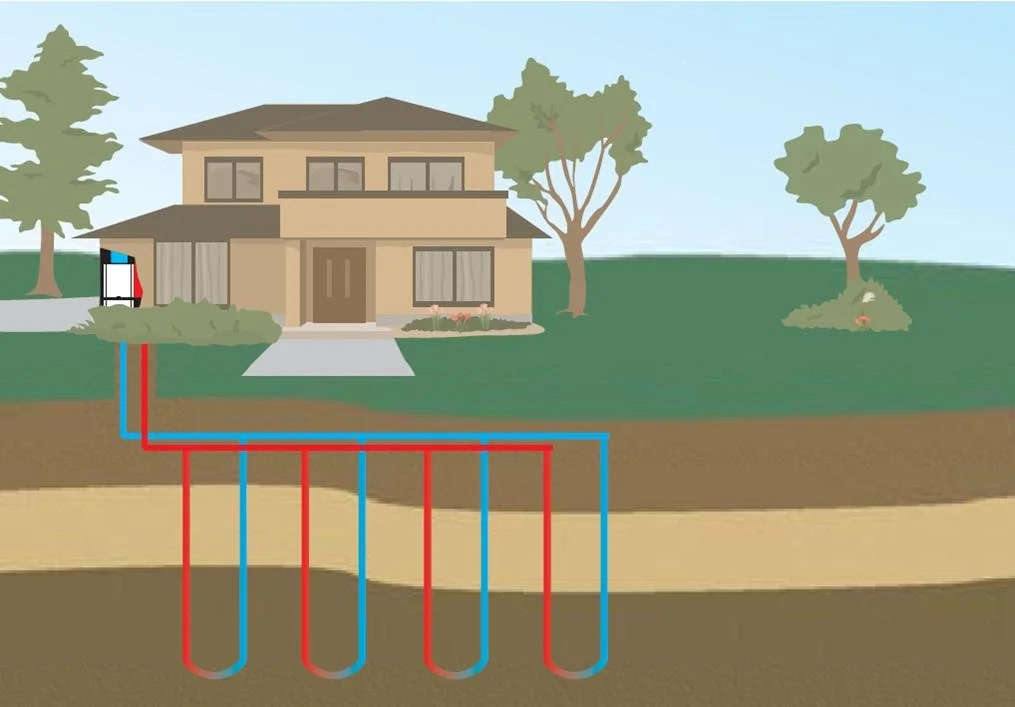
Ground Source Heat Pump
Ground source heat pumps can out perform other heat pumps as well as furnaces with superior efficiency.
Reliable Temperature
When it comes to heating our homes, we know that where we derive heat matters and with heat pumps this is no different. As noted in previous pages, air source heat pumps are a great choice for space conditioning as they provide efficient warming or cooling needs.
However, pulling warmth out of air that fluctuates greatly in temperature can be less than ideal. This is where ground source heat pumps shine.
Consider this: You are trying to heat a room to a comfortable 70 F when the ambient outside temperature is 40 (or 100 F). This is a wide temperature bridge. Now, consider that the ground stays at a constant temperature throughout the year (a few feet below grade), this temperature bridge has been greatly reduced. These benefits grow the wider the temperature differentials are and show up in overall energy used and of course, cost.
A ground source heat pump, like an air sourced unit, still relies on using a heat exchanger to pull heat from one medium into another. In this case, the refrigerants and water are pulling heat from the earth and delivering that to an indoor unit to be transferred into warm air, typically distributed through duct-work in a building.
Vertical Boring = Less Space Required
In temperate climates with existing housing, installing a ground source heat pump could be a major hurdle, not just for the wallet but also for the land area required, especially for a horizontal system.
Ground source systems may be best suited for yet to be developed neighborhoods, or those in more extreme climates with larger undeveloped properties. The largest geothermal installation project, completed to date is in Austin, Texas. This ‘geo-grid’ was built to serve 7,000 homes with bore holes reaching as far as 400 feet into the earth.
Ground source heat pumps are worth being considered with a fresh perspective, especially as vertical boring technology is becoming a space saving practice.
Cost Savings
As with air sourced heat pumps, ground sourced also provide regular cost benefits when compared to fossil fuel heating.
Geothermal heat pumps provide year-round comfort by offering both heating and cooling in a single system, and they have a longer lifespan compared to gas furnaces.
For those looking to reduce their carbon footprint and invest in a sustainable, long-term heating solution, a geothermal heat pump can be an excellent choice.
Market Outlook
Heat pumps continue to bring predictable growth, year on year
Globally, heat pumps are growing more common and cost effective. With an anticipated compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6%, ground source heat pumps will be increasingly common in the coming years. By 2024, the market was valued at nearly $8 billion and by 2030 is on track to grow to about $12 billion.
The global heat pump market (including air, water and ground) is expected to keep growing from $86 billion in 2024 and is project to reach $148 billion in revenue by 2030.
Additional Resources
Science Direct: Vertical-borehole ground-coupled heat pumps: A review of models and systems
Canary Media: Geothermal heat pumps are crazy efficient. Should you get one?
Habitat For Humanity: An Affordable 48-Home Single-Family Community in Northeast Austin
Research and Markets: $11.4 Billion Geothermal Heat Pumps Market Outlook
Grand View Research: Heat Pump Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Technology